If you want to successfully manage risk, it helps to use the correct risk terms and expressions. Many people use risk terms without realizing that they may not be using the right terminology.
It’s easy to become confused because sometimes the field of risk management uses similar terms for different purposes. For example, “Operational Risk Management” has a different meaning in the banking and insurance industry, compared to other industries (oil & gas, mining, manufacturing, chemicals, etc.).
Similarly, the term “audit” can refer either to an internal audit conducted by an organization itself, or an external audit performed by an auditing firm hired by the organization. Some people confuse the two when using the term “audit”. This is important because an internal audit and external audit may assess different things, and have different frameworks and workflows.
Recently, I came across another confusion between two terms: Internal Audit and Internal Control. The source of the confusion stems mainly from the fact that an internal audit assesses the effectiveness of controls put in place to mitigate risks. Let’s take a deeper look at both concepts.
Internal audit is a function performed at specific times
Many people in risk management use this simple formula to explain the difference between Internal Audit and Internal Control: Internal Audit is a function, while Internal Control is a system. Internal audits are performed at specific times to assess: 1) if the company has a good understanding of the risks that it faces, and 2) if the controls put in place to mitigate risks are effective. There is one very important distinction to be made: it is not the job of internal auditors to identify risks, nor to specify the controls that are needed. Internal Audit evaluates whether the process leading to the identification of risks is working well, checks whether controls already in place are working according to the way they are intended to, and evaluates an organization’s governance system and process.
Internal control is an ongoing system
Internal Control is made up of procedures, policies and measures designed to make sure that an organization meets its objectives, and that risks that can prevent an organization from meeting its objectives are mitigated. While the Internal Audit function is performed by internal auditors, Internal Control is the responsibility of operational management functions. Another point of contrast is frequency. An internal audit is a check that is conducted at specific times, whereas Internal Control is responsible for checks that are on-going to make sure operational efficiency and effectiveness are achieved through the control of risks. Some risk experts even say that Internal Control is a part of a company’s day-to-day management and administration.
The relationship between internal audit and internal control
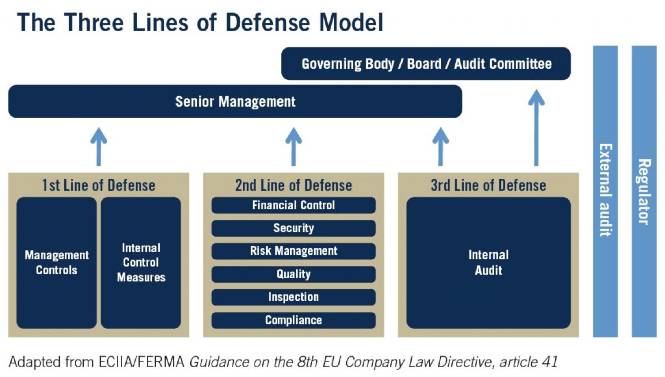
The best way to illustrate the relationship between Internal Audit and Internal Control is to show where they both fit in the Three Lines of Defense Model. Here’s an image of the model from The Institute of Internal Auditors:
Three lines of defense model from The Institute of Internal Auditors
Internal Control is part of the first line of defense because it is the responsibility of Operational Management, which itself is accountable to Senior Management. Internal Audit is part of the third line of defense. It even assesses the effectiveness of the first (Operational Management functions) and second (Risk and Compliance Management functions) lines of defense. Moreover, unlike Internal Control, Internal Audit may report directly to the Board of Directors and specifically the Audit Committee, in order to maintain a certain independence and objectivity when assessing other functions in the company that operate at the first two lines of defense.
Finally, if you are considering , knowing the difference between Internal Audit and Internal Control becomes even more important, because both must be managed in different ways due to their unique characteristics. Make sure that the software under consideration addresses the unique needs of both.