Transportation costs are a significant component of the overall supply chain costs. Therefore, supply chain and logistics managers must take advantage of transportation’s potential in terms of opportunities for cost reduction. In this article, we will be exploring one of the fundamental cases of market and supply allocation; it’s called the Transportation problem.
The goal is to satisfy demand, which means being responsive, while also being efficient, which means having the lowest transportation cost. Allocating supply sources to facilities properly has a considerable impact on your supply chain’s financial and operating performance. By doing it right, you will be managing production and inventory effectively, speeding processes, and improving customer service.
The Transportation Problem
The transportation problem is one of the subclasses of a linear programming problem in which the objective is to transport products stored in a facility (e.g. a warehouse) to different destinations or markets in such a way as to minimize total transportation cost while satisfying all the supply and demand constraints.
Here is a list of information needed to solve a transportation problem:
- Product demand at each destination facility.
- Facility locations and distances between each source and destination facility.
- Cost per kilometer traveled.
- The maximum storage capacity of each source facility.
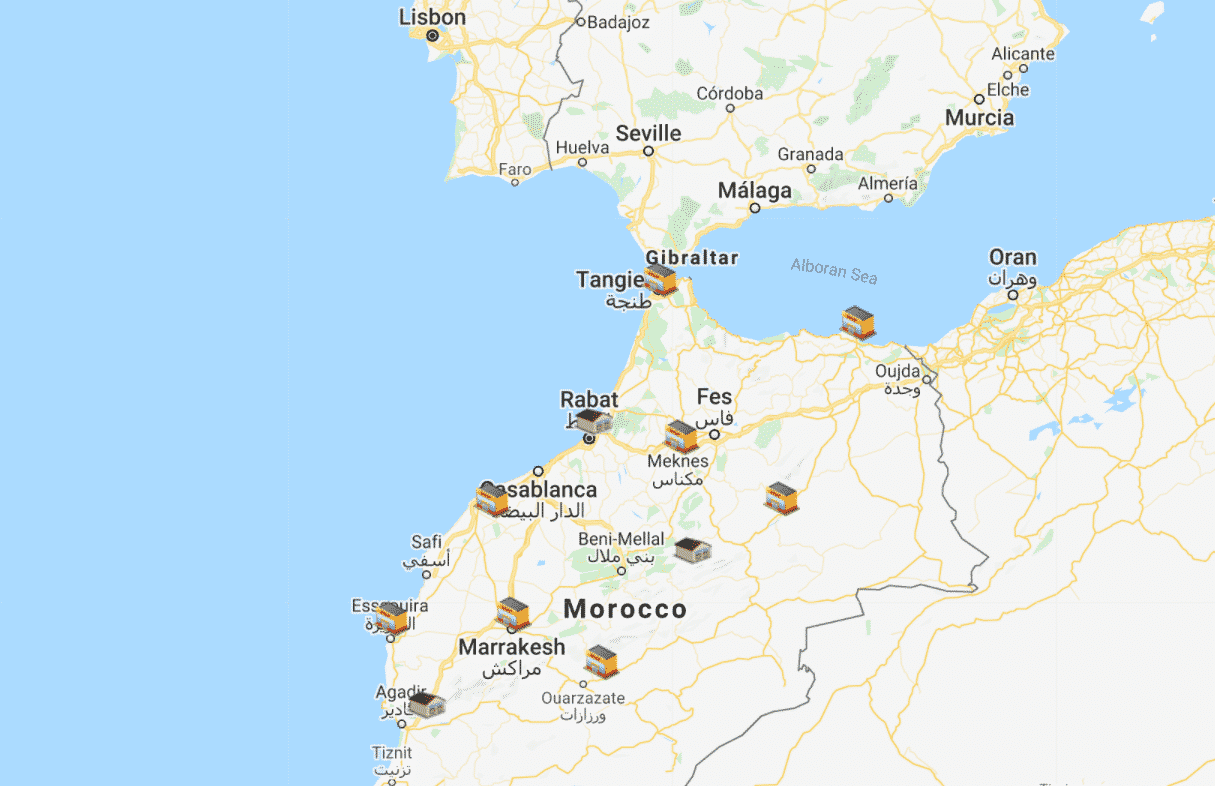
Below is the supply chain network we are going to use. It’s a simple network with two stages: there are three Distribution Centers, and the other eight facilities are Stores. Facilities are defined and their icons are put on the map using the SCM Globe supply chain modeling and simulation app. In the screenshot below you can see the facilities and the network of possible roads to use in delivering products from one facility to another.
We are glad to provide afree evaluation accountto instructors, students and supply chain professionals interested in exploring SCM Globe simulations — click here to request an account —Get Your Free Trial Demo
The supply chain model shown in the screenshot above can also be represented with an abstract network diagram like the one below: 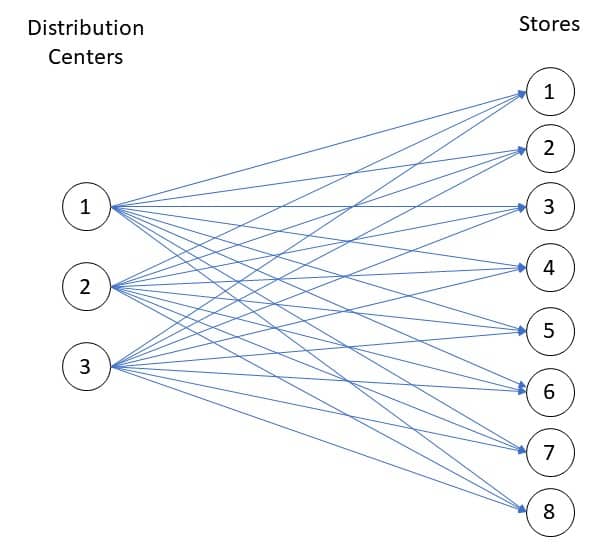
Moving to Excel Solver
Now that we have defined the problem and the network model, it’s time to move to Excel to enter the data and make our analysis.
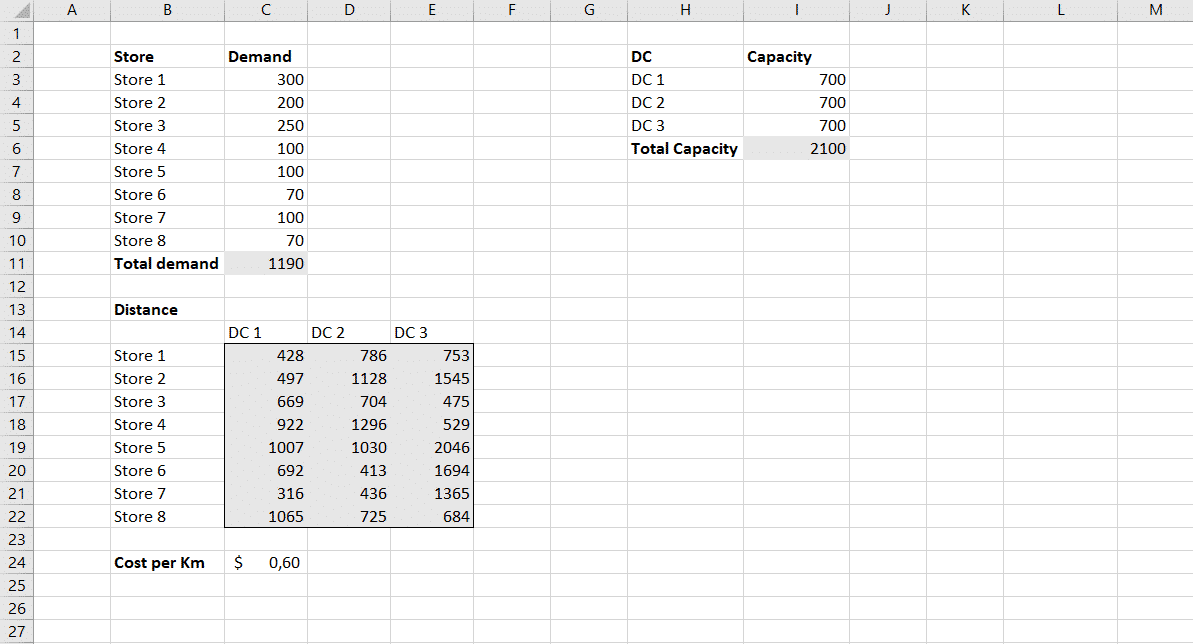
The first step in our process is to enter the data we need from the supply chain model in an organized manner. Click on each facility in the SCM Globe supply chain model to see information for product demand, storage capacity, etc. Start by entering each store’s demand; that gives us a total demand of 1190 units in this case. Then enter the unit storage capacity for each distribution center. That gives us a total capacity of 2100 units. We can easily see we have enough capacity to cover market demand.
The second step is to enter the distances between all sources and destinations (between DCs and Stores). To find these distances, create routes between each DC and each of the stores. At each DC define a truck and create routes for it to each store (you don’t need to save these routes, just create them to get distances to the stores). When you do this the route distances shown will be round trip distances, so divide these distances in half. The cost per Km is $ 0.9 which is a default value in the software for large trucks. You can change this default value to more accurately reflect current actual costs per Km based on your research. Later, after the solver shows which are the best routes to use, then you will come back to the supply chain model to create and save those routes.
Next, create the changing variables in your spreadsheet template. Remember, our goal is to find delivery quantities from DCs to stores that minimize transportation costs while still meeting store demand. Therefore, the changing variables in our case are the number of units moving on each route.

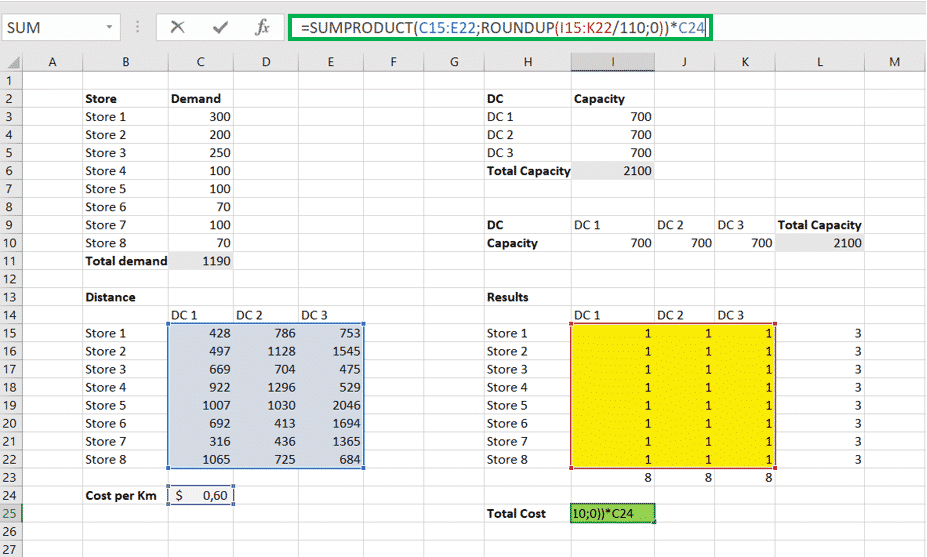
The decision variables that will be changing are colored in yellow. We can make the value in the yellow matrix zeros, but to make sure that our rows and columns sums are correct, we made them equal to one. The values on the right side of the matrix are the total quantity delivered to each store, and the values below the matrix are the total quantity that each DC will transfer. We also copied the DC’s and capacity matrix, and we pasted its Transpose. We did that so we can add quickly and easily the capacity constraint in Solver.
Before creating and running our solver model, we should define the total cost formula. Here, we have two options:
- The total transportation cost can be equal to the cost per Km multiplied by the distance of each route and then multiplied by the number of deliveries needed since vehicles have a maximum carry volume.
- If we have the cost per Km per unit, then the total cost will be equal to the cost per km per unit, multiplied by the distance of each route, and then multiplied by the number of units sent on those routes.
In our case, we only have the cost per Km traveled, and so we will use the first option. To know how many trucks we need to deliver the quantity incurred from one DC to a Store, we have to divide this quantity by the maximum carry volume of our trucks and round that number up (The ROUNDUP Function in Excel). In our example, we suppose that one large truck has a maximum carry volume of 110 units. The number of deliveries needed will be then equal to “ROUNDUP(I15:K22/110;0)”. And the total transportation cost formula is “SUMPRODUCT(C15:E22;ROUNDUP(I15:K22/110;0))*C24”.
If you have the cost per Km per unit, then the formula will be basically “SUMPRODUCT(C15:E22;I15:K22)*C24”. Something to keep in mind here is that, in this simple transportation problem, the cost per Km or the cost per Km per unit will not change the solution, but it only affects the total cost.
Creating and Running the Solver Model
Let’s define the objective function and the constraints of our model:
- The objective function: The objective of our model is to minimize the total cost.
- Constraints: First, we have demand constraints, therefore to meet demand, the total quantity delivered to each store must be equal to the demand of that store. Second, the quantity delivered from each DC must not exceed its unit capacity. And third, the decisions variable, which are the quantities delivered, must be an integer and greater than or equal to zero.
Now, let’s see how we can apply this to the Excel Solver add-in. First, go to the “Data” tab, and click on the “Solver” button that can be found on the right side. [If you have not installed the Solver yet visit this link to learn how to install it: https://www.solver.com/excel-solver-how-load-or-start-solver.]
Once the solver tab opens, we have to set the objective. In our case, we select the “I25” cell in green; this is our total cost. The variables that we are changing are grouped in the yellow matrix, and so we select this matrix in the second block.
Concerning the constraints, we have to click on the “Add” button. The three constraints created are shown in the figures below. After adding all these constraints, we have first to make unconstrained variables non-negative by selecting the checkbox. By respecting these installed constraints we can run our Solver model by selecting the Simplex LP (a solving method since our model is linear).

Our model is now ready, so click the “Solve” button. We can see that the decision variables and the total cost are changing. The result is a preliminary optimal solution for our transportation problem.

Interpretation of Results
We can verify results by seeing if we meet all demands and if capacity constraints are respected.
In this example, we got a total cost of $ 3,991.20, which is acceptable, but we notice that the only warehouse that will be using its max storage capacity is the DC Nbr 1. DC Nbr 3 is using 60% of its max storage capacity, and DC Nbr 2 is only using 10%. Hence the question: Do we need to open all three distribution centers for the next period?
One can say that by using only two facilities, the costs of operating facilities will decrease, but the transportation costs may increase. To find the optimal solution, we have to compare the total cost of two different scenarios. Which scenario offers the lowest total cost while still meeting store demand? In the first scenario, the company opens and uses all its DCs, paying all its fixed costs. In the second scenario, the company operates only two of its DCs while closing the third one.
Make copies of your original SCM Globe supply chain model and change them to reflect these two potential supply chain designs. Run those models in simulation to see how they work, and generate simulation data to create Profit & Loss Reports and KPIs. Compare the simulations and their performance reports. Get review and input from relevant parties, and pick the supply chain design that reviewers feel best meets the needs of the company in this situation.
Conclusion
Supply chain management is both a science and an art. In addition to numeric calculations, the role of professional judgment is also important as it can find growth opportunities, while numeric calculations find ways to reduce costs. Simulations help people explore different ideas and find new opportunities. Simulations bring together numeric calculations and professional judgment.
Situations change from month to month. This month’s optimal solution can quickly become next month’s big mistake. Companies plot their course each month by combining numeric calculations with professional judgment to navigate successfully through a constantly changing world.
[ See more about using the solver for supply chain route selection and scheduling in our blog post “Manage Your Transportation by Solving The Vehicle Routing Problem“ ]
Special thanks to Mr. Curtis Frye for the quality of his course titled: “Excel Supply Chain Analysis: Solving Transportation Problems” on LinkedIn Learning. We based our Excel demonstration on his way of organizing the spreadsheet template.
